41+ Background correction for images using imagej
Home » Art » 41+ Background correction for images using imagejYour Background correction for images using imagej images are ready in this website. Background correction for images using imagej are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Background correction for images using imagej files here. Find and Download all free photos.
If you’re looking for background correction for images using imagej images information related to the background correction for images using imagej keyword, you have pay a visit to the right blog. Our website frequently provides you with hints for seeing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video articles and images that fit your interests.
Background Correction For Images Using Imagej. Select Create Composite and click OK. 1 Calculating mean stained area and the standard deviation for each image 2 Taking the sum A of this. Without changing any settings move to a blank area of the slide and take an image. First check that the background is neutral.
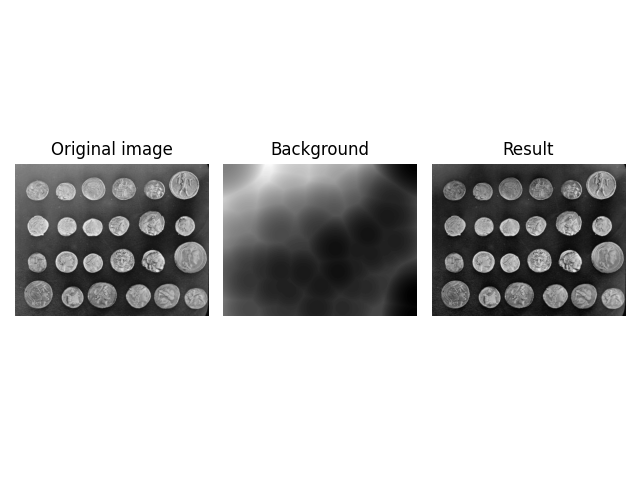 Use Rolling Ball Algorithm For Estimating Background Intensity Skimage V0 18 0 Docs From scikit-image.org
Use Rolling Ball Algorithm For Estimating Background Intensity Skimage V0 18 0 Docs From scikit-image.org
Select the fluorescent images in the appropriate R G and B channels and the DIC or similar image in gray channel. This method usually requires background correction of the image which can be done using the ProcessSubtract Background command. Ideally the mean intensity should be zero as the image is 8 bit with dark background. This displays the zero values blue and the 255 white values red. Alternatively you can carefully remove your slide and put in an empty slide to get a background image. Background correction can be done in several ways and is facilitated if the grey image has the PluginsLUTHi Lo indicator Hotkey.
Click on the new composite image to.
Automated background correction for batch quantification of images using a new ImageJ macro. Select Create Composite and click OK. But it is not the case for my sample. Figure 3 contains profile plots AnalyzePlot Profile of the first row of dots before and after background correction was done using the Subtract Background command with the rolling ball radius set to 25 pixels. 61 FLAT-FIELD CORRECTION 1. This method usually requires background correction of the image which can be done using the ProcessSubtract Background command.

Alternatively you can carefully remove your slide and put in an empty slide to get a background image. My problem is very basic - I have a stack of images and want to substract the background from each image based on a ROI. It only works for 8 bit grayscale images. ImageColorMerge Channels and the Merge Channels box will appear. Check this option to make sure that the image data after subtraction will never be below the background.
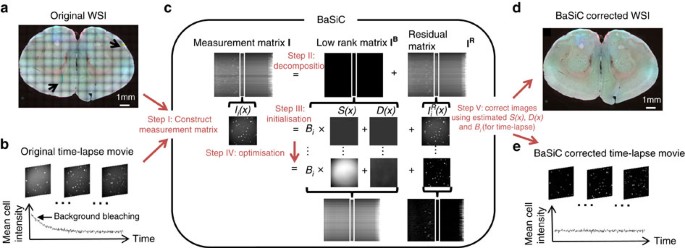 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Automated background correction for batch quantification of images using a new ImageJ macro. Select Create Composite and click OK. ImageColorMerge Channels and the Merge Channels box will appear. Draw a ROI in a white space. Without changing any settings move to a blank area of the slide and take an image.

So for each image measure mean ROI intensity and substract the value from. Select the blue channel of image 1 that you saved in task 1 and use the thresholding adjustment. Check this option to make sure that the image data after subtraction will never be below the background. Image Adjust Threshold First use the Auto button and then manually adjust the slider to see the changes. Figure 3 contains profile plots AnalyzePlot Profile of the first row of dots before and after background correction was done using the Subtract Background command with the rolling ball radius set to 25 pixels.
 Source: imagej.net
Source: imagej.net
Without changing any settings move to a blank area of the slide and take an image. Open both images in ImageJ. Background correction can be done in several ways and is facilitated if the grey image has the PluginsLUTHi Lo indicator Hotkey. Requires ImageJ version 123 or above. This displays the zero values blue and the 255 white values red.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Figure 3 contains profile plots AnalyzePlot Profile of the first row of dots before and after background correction was done using the Subtract Background command with the rolling ball radius set to 25 pixels. Change or check all Images are in 8-bit format. Select the blue channel of image 1 that you saved in task 1 and use the thresholding adjustment. But it is not the case for my sample. The difference between these is that a priori correction uses additional images obtained at the time of image capture while in a posteriori correction the additional images are not available and therefore an ideal illumination model has to assumed.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
If youre having trouble finding a completely empty area try de-focusing to blur-out the objects. The difference between these is that a priori correction uses additional images obtained at the time of image capture while in a posteriori correction the additional images are not available and therefore an ideal illumination model has to assumed. Select the fluorescent images in the appropriate R G and B channels and the DIC or similar image in gray channel. This is best done using a Region of Interest in an unstained area. Change or check all Images are in 8-bit format.

We implemented an ImageJ plugin that allows the user to compensate for the photobleaching to estimate the non-bleaching condition with choice of three different algorithms. To speed up the process with an image that has a more even background select a region of interest from the background and subtract the mean value of this area for each slice from each slice. Change or check all Images are in 8-bit format. ImageJ beginner here used the basic functions quite a lot but havent done anthing macroplugin related. But it is not the case for my sample.
 Source: imagej.net
Source: imagej.net
61 FLAT-FIELD CORRECTION 1. We implemented an ImageJ plugin that allows the user to compensate for the photobleaching to estimate the non-bleaching condition with choice of three different algorithms. Background correction can be applied while acquiring images a priori or after acquisition a posteriori. Without changing any settings move to a blank area of the slide and take an image. Open both images in ImageJ.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
But it is not the case for my sample. This is best done using a Region of Interest in an unstained area. Take your background image. ImageColorMerge Channels and the Merge Channels box will appear. This method usually requires background correction of the image which can be done using the ProcessSubtract Background command.
 Source: forum.image.sc
Source: forum.image.sc
The difference between these is that a priori correction uses additional images obtained at the time of image capture while in a posteriori correction the additional images are not available and therefore an ideal illumination model has to assumed. To understand whether the mean intensity varies actually due to sample configuration I need to first correct the background. Ideally the mean intensity should be zero as the image is 8 bit with dark background. Requires ImageJ version 123 or above. Problems with background substraction.
 Source: scikit-image.org
Source: scikit-image.org
Auto-contrast the result image. Check this option to make sure that the image data after subtraction will never be below the background. This method usually requires background correction of the image which can be done using the ProcessSubtract Background command. This filter works quite well for images collected under uneven illumination. Ideally the mean intensity should be zero as the image is 8 bit with dark background.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
ImageJ beginner here used the basic functions quite a lot but havent done anthing macroplugin related. Open both images in ImageJ. Auto-contrast the result image. Alternatively you can carefully remove your slide and put in an empty slide to get a background image. Background correction can be done in several ways and is facilitated if the grey image has the PluginsLUTHi Lo indicator Hotkey.
 Source: imagej.net
Source: imagej.net
With Disable Smoothing the unmodified image data are used for creating the background. If they arent then you need to adjust the image using background subtraction. 61 FLAT-FIELD CORRECTION 1. The difference between these is that a priori correction uses additional images obtained at the time of image capture while in a posteriori correction the additional images are not available and therefore an ideal illumination model has to assumed. With Disable Smoothing the unmodified image data are used for creating the background.

We implemented an ImageJ plugin that allows the user to compensate for the photobleaching to estimate the non-bleaching condition with choice of three different algorithms. The R G B values should be similar. The histogram matching method is a novel algorithm for photobleaching correction. The rolling-ball algorithm takes a lot of time. It only works for 8 bit grayscale images.
 Source: licor.com
Source: licor.com
Auto-contrast the result image. This displays the zero values blue and the 255 white values red. 61 FLAT-FIELD CORRECTION 1. Problems with background substraction. It only works for 8 bit grayscale images.

Automated background correction for batch quantification of images using a new ImageJ macro. Select the blue channel of image 1 that you saved in task 1 and use the thresholding adjustment. Change or check all Images are in 8-bit format. Automated background correction for batch quantification of images using a new ImageJ macro. Alternatively you can carefully remove your slide and put in an empty slide to get a background image.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Figure 3 contains profile plots AnalyzePlot Profile of the first row of dots before and after background correction was done using the Subtract Background command with the rolling ball radius set to 25 pixels. Background correction can be done in several ways and is facilitated if the grey image has the PluginsLUTHi Lo indicator Hotkey. Click Apply when you are happy with the image. Draw a ROI in a white space. Click on the new composite image to.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Click Apply when you are happy with the image. To speed up the process with an image that has a more even background select a region of interest from the background and subtract the mean value of this area for each slice from each slice. ImageJ beginner here used the basic functions quite a lot but havent done anthing macroplugin related. My problem is very basic - I have a stack of images and want to substract the background from each image based on a ROI. But it is not the case for my sample.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title background correction for images using imagej by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.
Category
Related By Category
- 46+ Background green screen for business
- 31+ Background images hd black samurai
- 42+ Background images for laptop aesthetic
- 16+ Background color blue and green
- 50+ Background for dark mode
- 15+ Autumn night landscape for windows 10 background
- 44+ Background images for parties
- 20+ Background images for motivational quotes
- 37+ Background dark undertow club
- 44+ Background images for a native indian love goddess